Editing of semantics |



|
|
Each map object can be assigned descriptive characteristics. For example, the own name or the height of an object. All these characteristics are described in the Semantics tab.
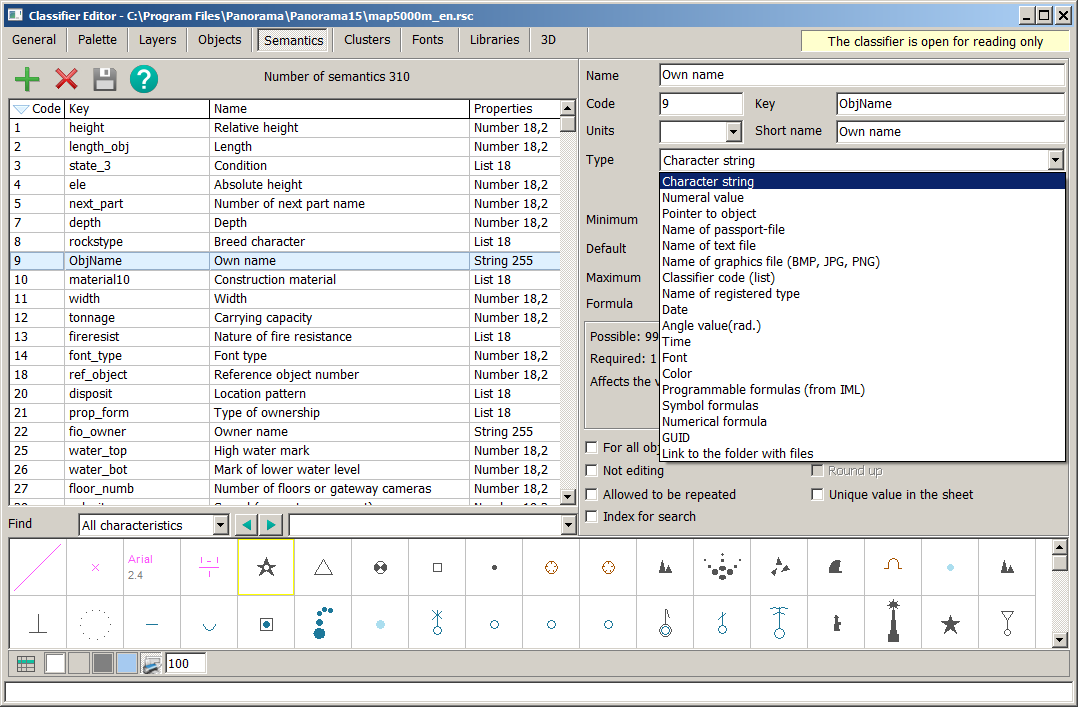
Each semantics has a description: name, alias, unique key, code, type, and so on. Semantics type determines what kind of data can be written into a given field. The following types of semantics are available: — character string; — numeral value; — pointer to object; — name of passport-file; — name of text file; — name of graphics file (BMP, JPG, PNG); — classifier code (list); — name of registered type; — date; — angular value (radians); — time; — font; — color; — programmable formulas; — symbol formulas; — numerical formula; — GUID; — link to the folder with files.
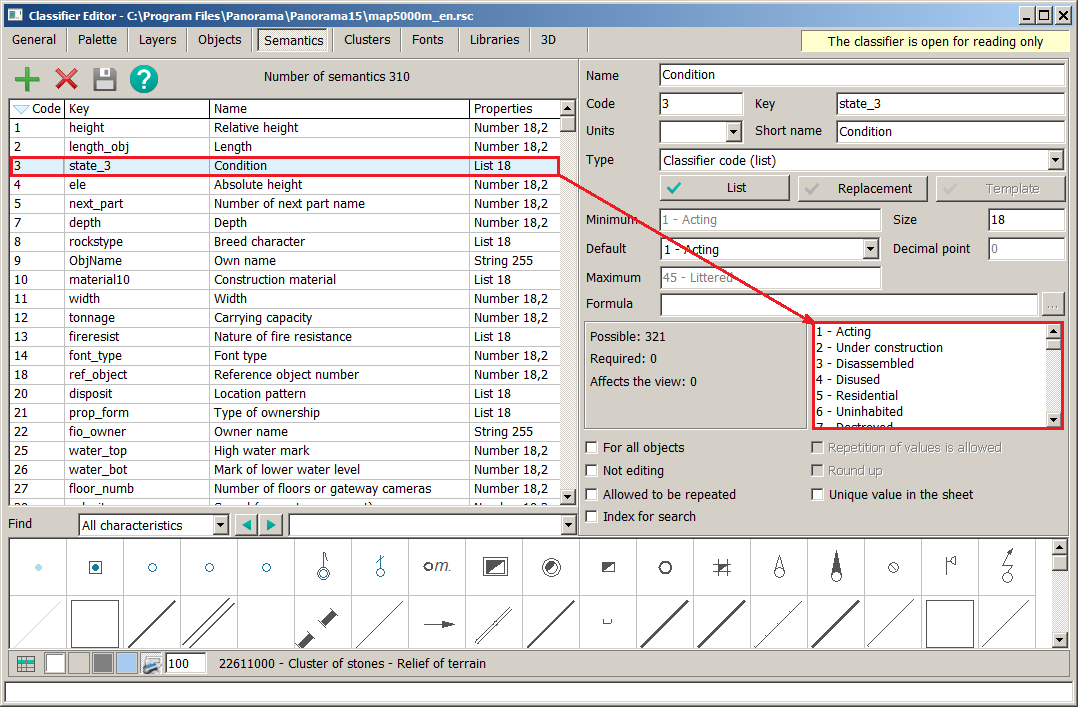
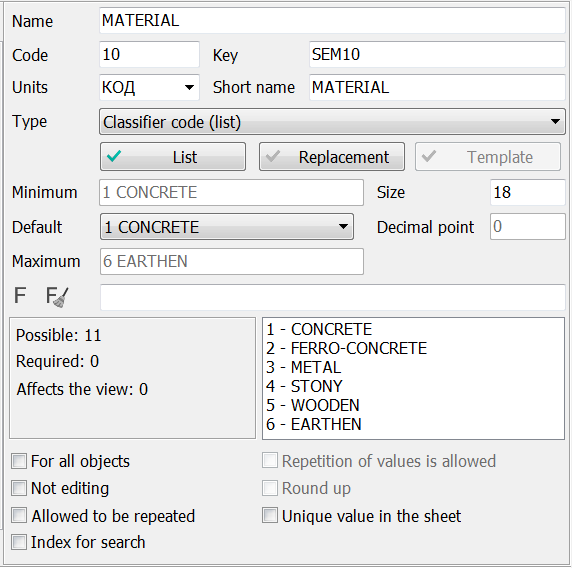
For each characteristic, a list of values can be created. At the same time, for numeral characteristics to one code usually there corresponds a range of values (for example, width of the river: up to 5м− 1, from 5 to 10 − 2 and so on), for symbolical characteristics to one code there corresponds one value (a structure material: a tree − 1, a brick − 2 and so on). For creating a list of values it is necessary to use the List button.
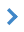
Semantics tab contains a list of classifier semantics in the form of a table of 4 columns: code, key, semantics name and properties. These fields are not editable. By clicking on one of the columns in the group, you can order (sort) the semantics. The lower right part of the dialog displays the objects for which the selected semantics is used. To go to the Objects tab, double-click on the required object.
To enter new semantics, click the Add semantics
In the right part of the Semantic Editing dialog, there are fields with semantic characteristics:
1. Semantic Name (255 characters) − an arbitrary character string. 2. Semantic Code (integer less than 65000) is used for identification and must be unique. Important! The range of semantic codes from 31000 to 33000 is reserved, so it is not allowed to create user semantics with these codes. 3. Semantic Key (string up to 15 characters) is used for naming fields in databases (it is allowed to include characters possible for field names in databases). The key can be used for identification and must be unique.
Attention! The semantic alias is used when exporting data to other formats as the field name of a database table. Therefore for it it is forbidden to assign keywords used in SQL-queries:
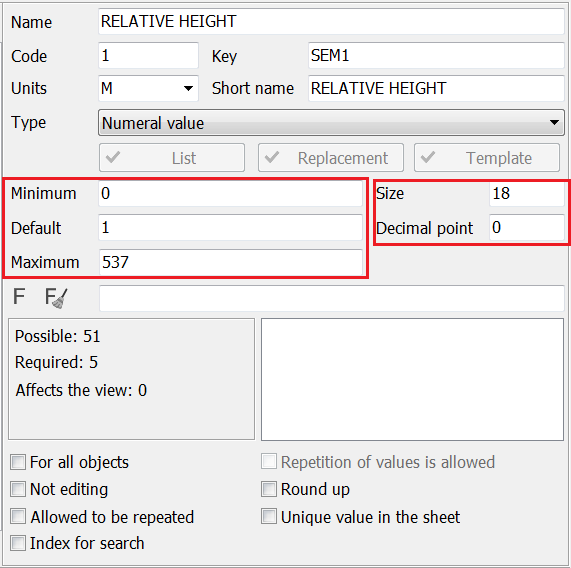
Units of measure are used for labeling the values of semantics. If semantics has no measurement (for example the Condition) the field should be empty. To select units of measure, you must select the desired value from the standard list or enter the required value from the keyboard. For semantics of type the numeric or code from the classifier, default values are entered. These default values are common to all objects. If semantics is mandatory for object, and the value is missing for some reason, the semantics of the object will be assigned a default value. When entering the values of the semantics of objects, the interval of possible values is set according to the minimum and maximum defaults. For values of type a code of the classifier the minimum and a maximum are set automatically. The user can only enter a default value.The size and precision of the semantic field value are used for formatted output of semantic values and unloading into the database.
Common for all objects field allows you to use the semantics for any classifier object without assigning it to each object. Not editing field is used in cases where the semantics of an object is created automatically and cannot be corrected by the user. Allowed to be repeated field is used when the object can have several values of semantics. For example, semantics the Type of vegetation of forest object can have values: a pine, a birch. Allowed value to be repeated field is used when an object can have several semantic values of the same semantics and these values can be repeated. Round up field allows, when displaying labels and values in various dialogs, to round up the value up to the number of characters specified in the Decimal field. For example, if the semantics stores the value 17.132, then 17.13 would be displayed for a precision of 2 digits. If the «Round up» property is enabled, 17.14 will be displayed. Unique value in the sheet field is used for semantics for which the uniqueness of values is important. For example: cadastral number of a plot or GUID. During the quality control of the map, the values of semantics with this flag are checked for uniqueness Index field allows you to speed up the search for semantics. Info button is used to display statistics on the use of semantics. For some semantics, values can be calculated using specified formulas. Formula To assign a symbolic semantics template, use the Template button. To assign a replacement for the semantics of the list type, use the Replace button. Changes are saved when switching to another semantics in the table, a dialog tab, or when pressing the Save |