Conversion of matrixes of heights with using the EGM2008 |


|
|
The task is designed to convert heights on the geoid (normal heights) from geodetic heights on ellipsoids: the global WGS-84 and GRS_80 (Geodetic Reference System 1980).
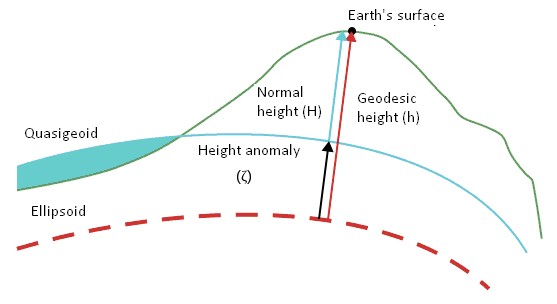
The geodetic (ellipsoidal) height of a certain point on the physical surface of the Earth is defined as the segment of the normal from the ellipsoid's surface to that point. Along with the geodetic latitude and longitude (B and L, respectively), it determines the position of the point relative to the specified ellipsoid.
Geodetic height depends on the location and parameters of the selected ellipsoid, which is why geodetic height is divided into two parts. One part characterizes the physical surface of the Earth relative to the reference surface, while the second, smoother part characterizes the difference between the reference ellipsoid and the geoid. The differences among normal, geodetic, and quasi-geoid heights are illustrated in the figure.
The task allows for converting matrices loaded from SRTM (Shuttle Radar Topography Mission) format, as well as other matrices in the WGS-84 geodetic height system, to normal heights (mean sea level). The task also enables the reverse transformation of matrices from normal heights (mean sea level) back to the WGS-84 geodetic height system.
For height conversion, the EGM2008 (Earth Gravitational Model) geoid models are used in the WGS-84 coordinate system. The geoid models are presented as matrices in MTW format with different cell sizes: with a resolution of 1 minute and with a resolution of 2.5 minutes. Bilinear or bicubic interpolation is used to obtain height corrections from the geoid model, based on user preference. |