Recommended python script structure |



|
|
At the beginning of the script, you need to import MAPAPI scripts and standard python scripts that will be used when writing functions. For example:
import ctypes import mapsyst import maptype import mapapi import seekapi import logapi import maperr import tkinter from tkinter import filedialog
After the MAPAPI script import commands, there are python functions that implement basic calculations using various MAPAPI functions. Below is the main function of the script (entry point).
An example of a calculated function:
# Move selected objects or one object def MoveObjectsByDxDy(hmap:maptype.HMAP, hobj:maptype.HOBJ, dx, dy) -> int: dpoint = maptype.DOUBLEPOINT(dx, dy)
if hobj != 0: return mapapi.mapRelocateObjectPlane(hobj, ctypes.byref(dpoint))
seekcount = seekapi.mapTotalSeekObjectCount(hmap) if seekcount == 0: mapapi.mapErrorMessageUn(maperr.IDS_OBJECTSNOTSELECTED, __name__) return 0
hwork = mapapi.mapCreateObject(hmap) percent = int(0) objcount = 0 hprogress = 0 if seekcount > 1000: hprogress = mapapi.mapOpenProgressBar()
logapi.mapLogCreateAction(hmap, hmap, logapi.TAC_MED_MOVE)
flag = maptype.WO_FIRST while (seekapi.mapTotalSeekObject(hmap, hwork, flag) != 0): flag = maptype.WO_NEXT
if mapapi.mapRelocateObjectPlane(hwork, ctypes.byref(dpoint)) != 0: mapapi.mapCommitObject(hwork) objcount += 1 newpercent = int(objcount * 100 / seekcount) if newpercent > percent: percent = newpercent if hprogress != 0: ret = mapapi.mapProgressBar(hprogress, int(percent), mapsyst.WTEXT(' Сдвиг объектов: ' + mapapi.IntToStr(objcount) + '/' + mapapi.IntToStr(seekcount)))
if ret == -1: break
if hwork != 0: mapapi.mapFreeObject(hwork) if hprogress != 0: mapapi.mapCloseProgressBar(hprogress)
logapi.mapLogCommitAction(hmap, hmap)
mapapi.mapInvalidate() return 1
After the auxiliary functions, there is a description of the main function of the script. For example:
# Move selected objects or one object def MoveObjects(hmap:maptype.HMAP, hobj:maptype.HOBJ) -> float: #caption:Сдвинуть объекты на заданные смещения dx,dy if hobj == 0: seekcount = seekapi.mapTotalSeekObjectCount(hmap) if seekcount == 0: mapapi.mapErrorMessageUn(maperr.IDS_OBJECTSNOTSELECTED, __name__) return 0
root = tkinter.Tk() root.title("Сдвиг объектов")
dx_label = tkinter.Label(text="Смещение по X (вверх): ") dy_label = tkinter.Label(text="Смещение по Y (влево): ") dx_label.grid(row=0, column=0, sticky="w") dy_label.grid(row=1, column=0, sticky="w")
dx_value = tkinter.IntVar() dy_value = tkinter.IntVar()
dx_entry = tkinter.Entry(textvariable=dx_value) dy_entry = tkinter.Entry(textvariable=dy_value) dx_entry.grid(row=0,column=1, padx=5, pady=5) dy_entry.grid(row=1,column=1, padx=5, pady=5)
def CallMoveObjects(): MoveObjectsByDxDy(hmap, hobj, dx_value.get(), dy_value.get()) root.destroy()
message_button = tkinter.Button(text="Выполнить", command=CallMoveObjects) message_button.grid(row=2,column=1, padx=5, pady=5, sticky="e")
root.eval('tk::PlaceWindow . center') root.mainloop() return 1
There may be several main functions in the script file. The main functions have one set and the type of parameters and the type of return value:
def MoveObjects(hmap:maptype.HMAP, hobj:maptype.HOBJ) -> float:
where: hmap - identifier of the currently open document for which the script is being executed hobj - identifier of the selected object, or null
The return value is of type float (in C++, this corresponds to double) to obtain the results of simple calculations. At the end of the line with the declaration of the function, a comment can be specified to write it into the list of scripts:
def MoveObjects(...)-> float: #caption:Сдвинуть объекты на заданные смещения dx,dy
The called function can perform some action on the passed object if the identifier is not zero, or on selected objects if the user has selected some objects on the map.
if hobj == 0: seekcount = seekapi.mapTotalSeekObjectCount(hmap) if seekcount == 0: mapapi.mapErrorMessageUn(maperr.IDS_OBJECTSNOTSELECTED, __name__) return 0
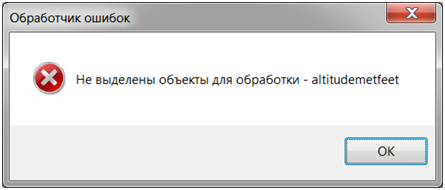
If an object is not passed or objects are not selected on the map, the script may output a message that the input data is not specified. The example shows the IDS_OBJECTS NOT SELECTED code - No objects are selected for processing.
To enter additional data processing parameters, dialogs based on a standard tkinter component can be called. It is desirable to select from the main function that calls the dialogs, a function that performs the basic data processing with all specified parameters. This will allow you to create scripts that work in automatic mode according to ready-made parameters that can be integrated into complex algorithms for automatic data processing.
For each group of operations, its own transaction can be formed, which will allow you to cancel the entire operation in the future, if necessary.
logapi.mapLogCreateAction(hmap, hmap, logapi.TAC_MED_MOVE) ... logapi.mapLogCommitAction(hmap, hmap)
When sequential processing of objects, the next object is read that satisfies the set filter.
flag = maptype.WO_FIRST while (seekapi.mapTotalSeekObject(hmap, hwork, flag) != 0): flag = maptype.WO_NEXT
If the operation is successful, the object can be saved on the map.
if mapapi.mapRelocateObjectPlane(hwork, ctypes.byref(dpoint)) != 0: mapapi.mapCommitObject(hwork)
To work with a map object, you need to create a program object (container) into which the processed map object will be read, and at the end of the work, release it.
hwork = mapapi.mapCreateObject(hmap) ... if hwork != 0: mapapi.mapFreeObject(hwork)
To display the changes made in the map window, you can call the image update function.
mapapi.mapInvalidate()
|