Checking of absolute elevations |


|
|
This task is designed to control vector map objects containing values of absolute terrain elevations and hydrographic depth values. The task also allows checking the presence and planned position of objects with absolute elevation within closed contour lines.
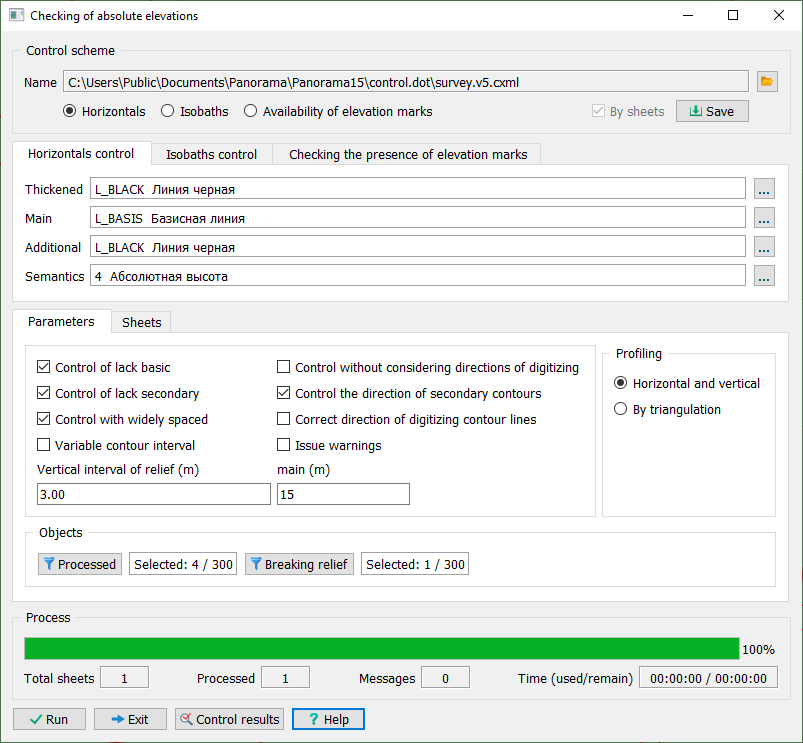
When performing the task, control schemes corresponding to classifiers of maps of various scales are used. The types of control specified in the dialog, their parameters, as well as the composition of processed objects are saved in an XML file in the common folder of system task parameters c:\users\public\documents\panorama\. The scheme file name has the cxml extension and is formed by the classifier name, for example: 50t05gm.cxml. The use of control schemes allows for step-by-step verification of relief objects in various modes.
The control parameters specified in the dialog can be saved in the scheme file using the Save button; to select a previously configured scheme, use the ... button in the Control Scheme block.
The Processed button in the Objects block is used to specify the composition of map objects to be checked. By default, all linear, areal, and point objects with absolute elevation semantics are processed. The Breaking relief button in the Objects block is used to specify the composition of linear and areal objects that disrupt the sequence of heights (for example, areal rivers, cliffs, quarries, ravines, and others).
As a result of the task, a control message protocol is created for the processed sheets of the area, which can be viewed in the Map Editor task — Measurements and Control\View Control Results mode. The protocol line contains information about the numbers and elevations of objects that are not coordinated by codes, height, or digitization direction. The "-" (minus) sign at the elevation value indicates the top-to-bottom digitization direction, the "+" (plus) sign indicates the bottom-to-top digitization direction.
The task performs the following types of control: — control of contour lines; — control of isobaths; — control of elevation points presence. |