Building a route network |



|
|
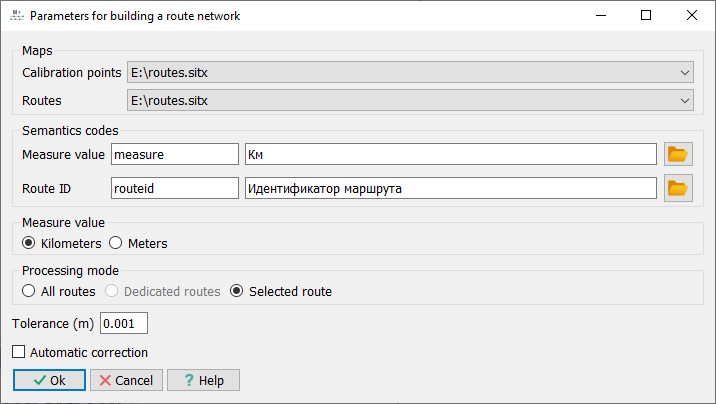
The calibration mode can be performed for a selected route, a group of highlighted routes, or all routes available on the map. Before starting the process, processing parameters are set in a special dialog: — selection of the route map and calibration points map, selection of the connection semantics (route ID), semantics of the linear measurement value; — setting the maximum allowable deviation of a point from the route; — choosing the units of measurement for the initial linear measurement values (meters or kilometers); — selecting the processing mode (Selected Route, Highlighted Routes, All Routes).
In the case of processing highlighted routes, before activating the process, the routes to be processed are highlighted on the route map.
Dialog for setting parameters for route construction procedure
During calibration, calibration points are used for a route that have a route identifier identical to that of the route being processed. For each route being processed, a list of calibration points is generated based on the matching route identifier, and the distance to the route is checked for compliance with the maximum allowable deviation. Additionally, a check is performed for the sequential increase of the linear measurement value as one moves away from the start of the object, and points with identical linear measurement values are selected. When processing in "All Routes" mode, a general data check is conducted before starting the processing. This includes verifying the presence of route identifiers for both routes and calibration points, as well as ensuring that calibration points have linear measurement values.
During the calibration process, the direction of the route is checked and automatically corrected if necessary (in accordance with the direction of increasing linear measurement values of the calibration points located on it). If the direction of the route is changed, a corresponding record is added to the processing protocol. If there is no calibration point at the first point of the route, it is automatically calculated. If the linear measurement value at the calculated point is negative, a corresponding record is made in the protocol and the processing of the route is terminated.
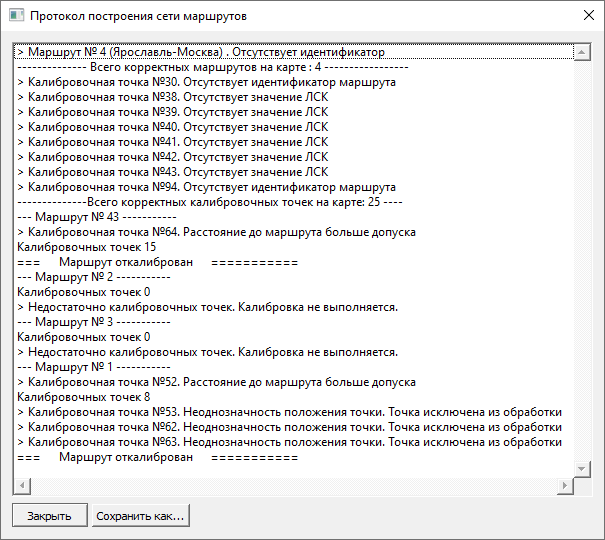
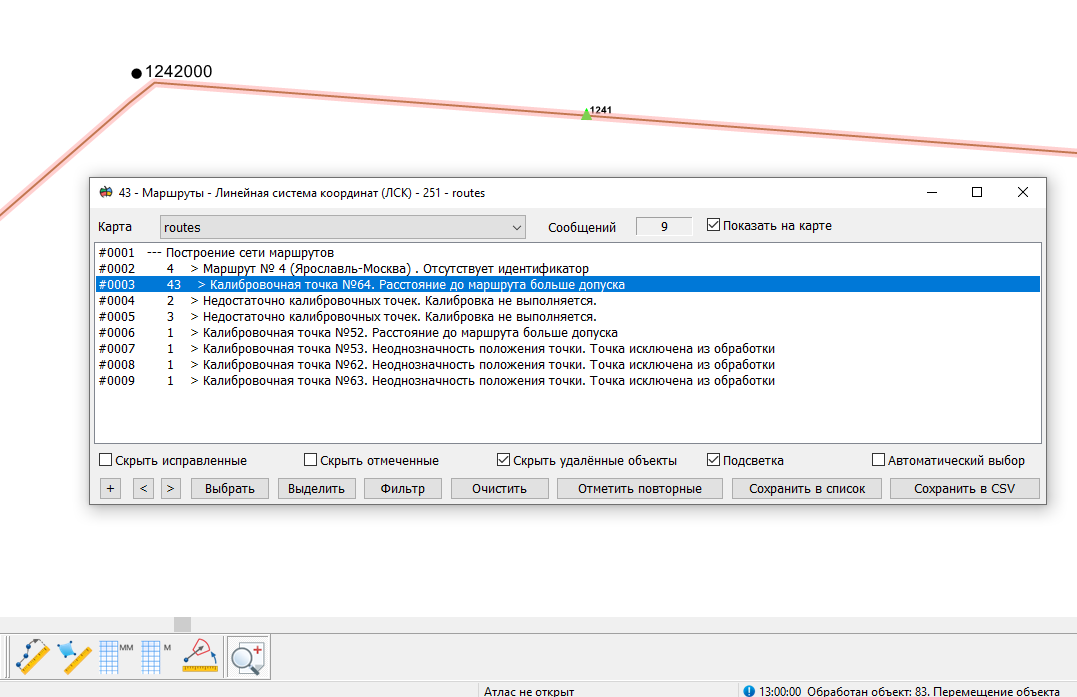
In the case of processing individual routes, calibratable routes are sequentially selected on the map and processed. When processing a group of highlighted routes, a sequential iteration and processing of previously highlighted routes is performed. When processing all routes, a sequential iteration and processing of all routes available on the map is carried out. At the end of processing, a text protocol is generated, which can be saved as a text file, along with an interactive protocol that allows for analysis and correction of errors.
Text calibration protocol
Error analysis using interactive protocol |
 The construction of a route network includes the verification of the correctness of the initial data and the calibration of the routes. Calibration of the routes involves entering the linear measurement value, calculated from the calibration points, into the coordinate M for each point of the route geometry. The initial data for constructing routes consists of a map of the original axial lines (route map) and a map of calibration points. Both maps must be open in the current document. The order of adding maps to the document does not matter.
The construction of a route network includes the verification of the correctness of the initial data and the calibration of the routes. Calibration of the routes involves entering the linear measurement value, calculated from the calibration points, into the coordinate M for each point of the route geometry. The initial data for constructing routes consists of a map of the original axial lines (route map) and a map of calibration points. Both maps must be open in the current document. The order of adding maps to the document does not matter.