Editing the cluster table |



|
|
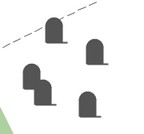
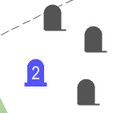
Cluster is an aggregation of several homogeneous elements that can be considered as an independent unit with specific properties. Accordingly, a cluster of map objects is a symbol used to represent multiple homogeneous map objects that start to overlap and stack on top of each other as the scale decreases. When displayed on a map at a large scale, objects are represented by their symbols. As the scale decreases and more than one object of a specified type is grouped in a cluster zone, their conventional symbols will automatically be replaced by a symbolic cluster sign, the center of which will have the averaged coordinate of the objects within it. When the scale changes, the configuration of clusters automatically changes.
An algorithm for automatic clustering is implemented to display densely located point symbols on a map. When the map is displayed, the territory is conditionally divided into cluster zones, forming a grid of clusters. The cluster grid is created with a specified step (the width and height of the cluster zone) in millimeters of the image. At each scale, this step is calculated in meters proportionally to the display scale. For example, at a scale of 1:5000, the grid may have a size of 500 meters, at a scale of 1:2000 - 200 meters, at a scale of 1:1000 - 100 meters. Since the denominators of the display scales are not multiples of 2, the cluster grids are not multiples of each other either. Therefore, an object at different scales may fall into zones of neighboring territories. Consequently, neighboring clusters at different scales "exchange" objects.
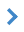
Let's consider the grid in one dimension simplistically: — the first row contains symbolic signs of objects (*); — the second row represents divisions of the grid for a scale of 1:1000; — the third row for a scale of 1:2000; — the fourth row for a scale of 1:5000.
The number of objects in clusters for each scale is indicated in parentheses:
According to this scheme, it can be observed that central clusters for a scale of 1:1000 contain 2 and 3 objects. For a scale of 1:2000, there is one central cluster containing 5 (2 + 3) objects. For a scale of 1:5000, the central cluster is absent. Its contents are divided into neighboring clusters 4 (2 + 2) and 5 (3 + 2).
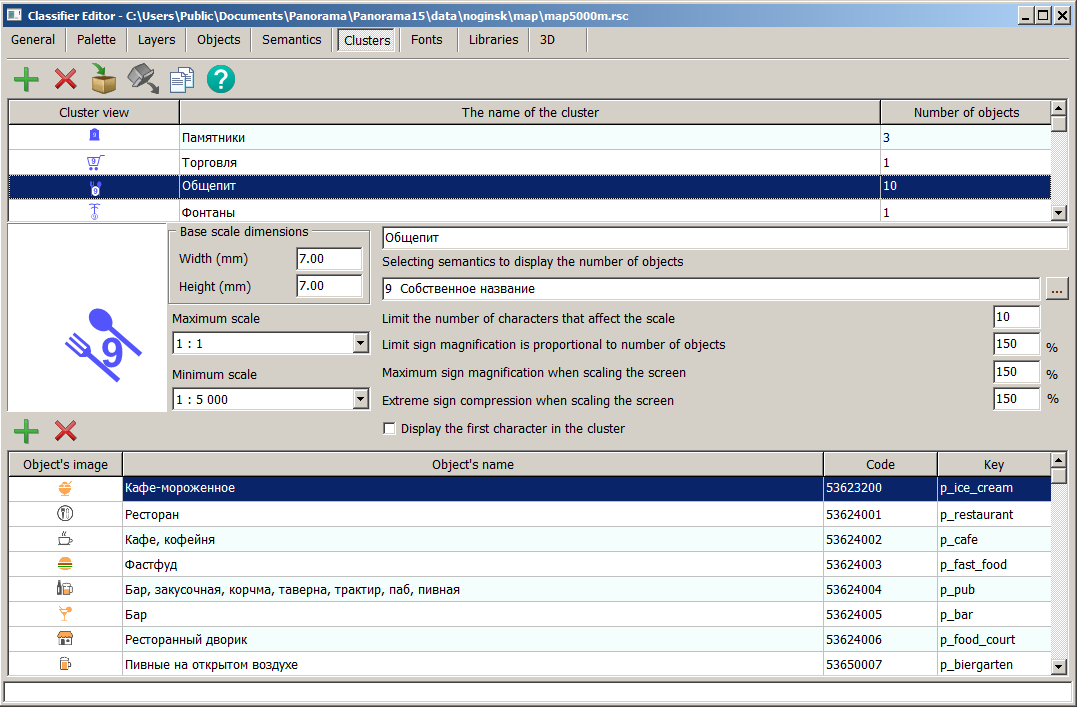
The Clusters tab displays a list of classifier clusters.
To create a cluster, you need to: 1. Select the Add Cluster mode 2. Enter the name and necessary parameters for the cluster. 3. Add objects from the classifier that belong to the cluster using the Add Object to Cluster sub-mode To remove types of objects that should not be included in the cluster, you can use the Remove Object from Cluster sub-mode
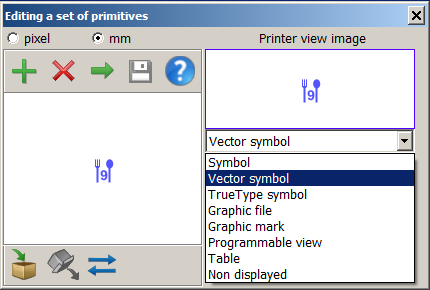
To create (edit) the symbol of the cluster, double-click with the left mouse button in the symbol view window to bring up the primitive editing dialog. In this dialog, you can select the required primitive and click the Parameters button.
The conditional symbol of the cluster can be programmable, allowing for various ways to distinguish the cluster type and change the symbol properties depending on the number of objects in the cluster (quantity label, symbol size, brightness, and so on). If a user uses a vector symbol for the cluster's appearance, they can create a text string to indicate the number of objects in the cluster, which is loaded into the semantics to display the quantity of symbols in the cluster (by default, this is semantics 31109). The semantics can be changed by pressing the selection button or clicking on the field with the semantics name.
When setting the property Display the first symbol in the cluster, the first object in the cluster will be displayed first in the cluster symbol position, followed by the cluster icon. In this case, the cluster icon may only contain the number of objects or other complementary elements of the conditional symbol. Various semantics can be taken into account when drawing an object, including references to graphic files, making the generalized symbol more complex and informative.
The parameters Width and Height represent the size of the cluster area horizontally and vertically in millimeters on the map for combining symbols in a cluster. When entering these dimensions, it should be noted that the zone size should be at least twice as large as the cluster symbol size.
The maximum number of symbols affecting the scale indicates the number of objects combined in a cluster from which the cluster symbol size no longer increases.
The maximum percentage increase in the cluster symbol size can range from 100% to 400%. To prevent the cluster symbol size from increasing depending on the number of objects being combined, set the option for proportional symbol enlargement based on the number of objects to 100%. Clusters can be created by copying The cluster description can be copied from another classifier via the clipboard. To do this, place the selected cluster in one classifier into the clipboard
Maps with clusters configured in the RSC classifier are automatically supported in all desktop and web applications, as well as in applications developed in GIS ToolKit and GIS Constructor. During high map congestion, symbols with similar meanings can be grouped together, and under certain conditions, instead of displaying multiple symbols, one summarizing symbol can be shown.
|