Metric |



|
|
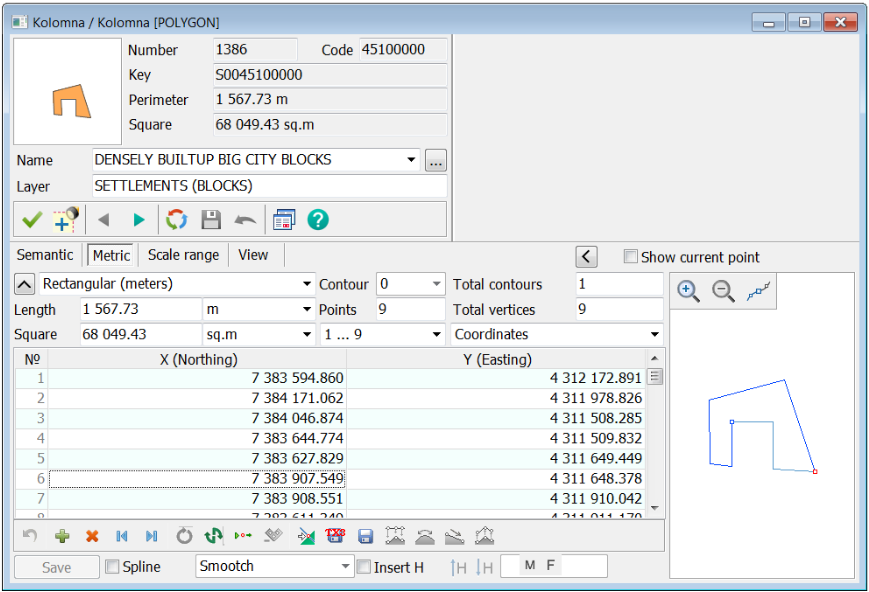
Displaying the object metric (sub-object) includes a number of statistical characteristics, as well as the coordinates and heights of its points and a schematic displaying the contour.
The following characteristics of object (subobject) are displayed: — number of subobjects in the object; — number of the displayed subobject (object has number 0); — number of points in the object (subobject); — distance between a current and next point of the object (subobject); — directional angle, azimuth, left rotary angle, right rotary angle from the current to the next point of the object (subobject) and rhumb.
The coordinates of the metric's points can be displayed and edited in different units: — in meters in a rectangular coordinate system; — in pixels in a rectangular coordinate system; — in radians in the geodetic coordinate system; — in degrees with an accuracy of 1E-6 - 1E-7 in the geodetic system of coordinates; — in degrees, minutes, seconds in the geodetic coordinate system.
When changing the coordinates of an object by changing the distance and angle, the coordinates of the point following the current one are corrected. The coordinates of the first point of the metric cannot be corrected by this method. If the metric of the object is the two-dimensional one, then you can add height to the coordinates. For this purpose it is required: — expand the window of help information about the object and enable the Insert H mode or select the corresponding item Insert H of the pop-up menu; — enter the height value in the field
In order to add a metric characteristic, it is necessary to choose modes
Further, by editing, you can set different heights in specific points of the object. To edit the heights in the metric of an object, you must first expand the reference information window about the object. This can be done by clicking the right mouse button above the dialog and selecting the Full-screen Object Information item in the pop-up menu, as well as by double-clicking the left mouse button above the dialog title. Deleting the selected coordinates of the object by the list. When coordinates are selected in the table, the selected area is synchronously highlighted on the scheme.
Modes of operation with the object metric
Additional pop-up menu modes
A general description of the metric is contained in the Object metric section.
|