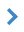
Adding a specified value of a given semantic attribute to all selected objects |



|
|
1. Using the map object search/selection dialog, set the list of objects to be processed and click the Select button. 2. Activate the semantic addition mode by clicking the corresponding button on the Semantics toolbar in the Map Editor. 3. Specify the name and value of the attribute to be added. Note that semantic attributes can be either repeatable or non-repeatable. If the selected semantic attribute can have multiple values for a single object (e.g., vegetation type: birch, oak), you must specify how the program should handle cases where the edited object already has this attribute (skip or add another value). 4. Click the Execute button.
All selected objects will be processed, even if they are located on multiple maps.
Constructing a string value using other semantic attributes
A string value can be dynamically generated based on the values of other semantic attributes of the object.
To do this, format the string as follows: After the %# symbols, specify the semantic code (a number). Inside [ ], provide the default value to be inserted if the object does not have this semantic attribute. No more than 16 insertions are allowed. The rest of the text can be in any format.
Example: Input string: "house No %#45[n/a] cond. %#3[not specified] (%#47[])"
This will use three semantic attributes of the object: Semantic 45 – HOUSE NUMBER (string) Semantic 3 – CONDITION (classifier type) Semantic 47 – FUNCTIONAL PURPOSE (string) Numeric semantic values are formatted according to the rules specified in the classifier.
Possible final results for a given object: "house No 5 cond. not specified ( )" "house No 7-a cond. RESIDENTIAL (pharmacy)" "house No n/a cond. not specified ( )"
|

