Maps of landmarks |



|
|
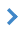
Maps of landmarks are intended to control the troops with use of communication facilities. They are made in scale 1:200 000 by the digital topographic maps, remote sensing data, materials of field geodetic works. As landmarks in a strip (area) of possible actions the clearly visible local objects are chosen (a barrow, a separate stone, crossroads, strongly prominent buildings, etc.), which the enemy cannot destroy and concerning which it is possible to transfer targeting. At choice of landmark on a map it is necessary to consider visibility of the chosen object from the observation post: a separate building (izba) - is discerned from 5 kilometers, the communication line post - is discerned from 1 kilometer. Landmarks are selected and are numbered from right to left and by the borders - from himself towards the enemy. The number of landmarks must be a little. In the company, platoon - two or three landmark, in the squad - one or two. In defense, there may be more. To each landmark the number is assigned. One of landmarks is assigned the main one (being on the basic direction or in the centre of a strip of possible actions). All landmarks of the senior commander observed from the command-observation post of subordinated commander, are mandatory for him , and for them numbers are stored that are assigned by senior commander. During the offensive, in process of moving forward, new landmarks are appointed. In defense, landmarks are selected as in front of the forefront, and in the nearest depth of the defense of own troops.
These maps of landmarks are imported from files obtained from geodetic instruments and remote sensing devices. These data are: - pointers of the commanding heights, geodetic points, crossroads, separate buildings, pillars, trees. Data of measurements is put above a topographic map into a separate map of landmarks with the classifier operator.rsc. Loading the data of field geodetic works is performed from the files received in field conditions on geodetic devices, equipped with means of electronic processing. Text files received from devices, should contain direct coordinates of points (X, Y, H), which the program puts onto the output map in format SIT in the form of point or linear objects. Additional signs are put by means of the map editor. |
