Dilating low-contrast regions |



|
|
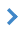
Each iteration of dilating is carried out as follows: - at first the search of extreme pixels of raster regions of low-contrast classes is carried out; - for each extreme pixel (it is marked in red) all classified pixels are defined, that fall within the window of scanning (the green pixels which fall into the blue circle of the scanning window); - by these pixels the average color is calculated; - then not classified pixels are determined, that fall within the window of dilating (yellow pixels); - if the color of all not classified pixels belonging to the window of dilating, differs from the average less than onto the specified tolerance, then all of them join the classified region.
Dilating the region:
Before performing the step for each class of low-contrast, you must set the number of iterations, the size of the scanning window, the the size of a dilating window and tolerance of deviation in color (valid values from 1 to 255). Parametres are selected depending on the source image. At the first running it is recommended to set the following values of parametres: - specify the number of iterations two times more than number of iterations of erosion; - set the same size of the scanning window, as at classification; - specify the size of dilating window two times less than the window of scanning; - set the tolerance of deviation of the color in the window of dilating concerning a scanning window in 20. The color deviation is calculated by the channels chosen in the list: Channels for calculating deviation of color. Tolerance of deviation in color has the greatest value. If it has too small value the low-contrast regions practically will not grow, if the value is big, the low-contrast regions will begin to penetrate into contrast regions and into each other.
Results of dilating:
Parameters of dilating:
|



