Choice of interpretive features |



|
|
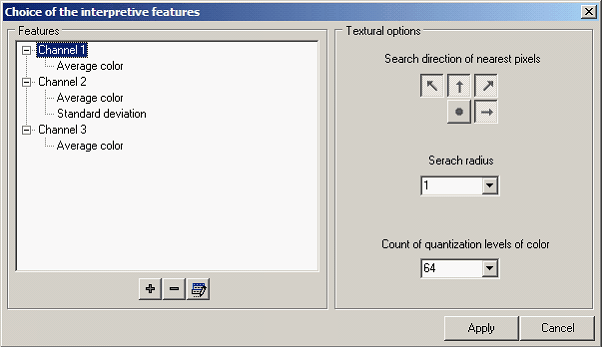
Dialog for Choice of interpretive features:
Under the interpretive features statistical and textural features are understood calculated by the color of pixels that fall within the limits of the scanning window, onto the selected spectral or calculated channel (an average or NDVI). They are:
- average color - standard deviation - textural energy - textural entropy - textural contrast - textural dissimilarity - textural homogeneity - textural inverse different moment (square-law homogeneity) - textural correlation
, where I - color of pixel of the chosen spectral channel; N- number of pixels in the scan window; P- an element of the adjacency matrix - a normalized number of pairs of pixels belonging to a scan window;
Textural features characterize the number of repetitions of the same pairs of pixels in the scan window. Energy and entropy depend on all repetitions of pairs pixels. Contrast, homogeneity, dissimilarity are the most sensitive to the number of pairs of pixels with the maximum relative difference. Correlation characterises homogeneity of repetition of pixels pairs. For practical application one feature from each group is selected. It is necessary also to consider the correlation is calculated considerably slower than the other textural features. The values of calculated textural features are highly dependent on the rules of a choice of pairs of neighboring pixels. The direction and distance of search of neighbours for each pixel of a window are set in the appropriate parameters of dialog. Also, the result may be influenced by level of color's quantization. Researches have shown that it is expedient to lead the real depth of color's quantization in a raster to the depth of color in the range from 24 to 64. Depth of color has the greatest influence on the calculation of the energy and entropy. Interpretive features can be calculated by any color component of pixels. You have three options: - real spectral channel of a raster; - an average from several chosen channels; - value of NDVI index, calculated by any two channels of a raster. Interpretive features are added, edited and deleted on channels. Adding features onto the channel is performed by pressing the button
Dialog of adding the interpretive features:
For editing the features on the channel it is necessary to choose the channel in a tree of features and to press the button |