General data |


|
|
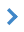
Procedure of creation of thematic cartograms is intended for forming graphic representations, visually illustrating a ratio of values of the chosen characteristic for separate objects of an electronic map. Cartogram (choropleth map, cartogram, chorogram, chorisogram) - - a map, showing distribution of relative parameters (density, intensity of any phenomenon, specific sizes, etc.) on certain territorial units, more often - administrative; - one of ways of the cartographical image, used for display of relative statistical data by way of filling contours of territorial division (usually administrative units) by color solids of different tone, by shadings (cross-hatch line pattern) of different density according to the accepted interval scales. Means of automation allow to build Cartogram in so-called continuous, or without-interval scales (choropleth maps without class intervals, continuous-tone cartogram) when the density is put in exact conformity to size of a mapped parameter. (Explanatory dictionary on geo-informatics) Cartogram - a thematic map on which the area's objects (polygons) are painted into different colors depending on corresponding to them values of the analyzed characteristic. Cartograms can be colored (filling of polygons by various colors), strobe (drawing onto polygons of a various kind of shadings) and point (filling of polygons by files of points of the various size and a degree of a condensation). Color cartograms can be gradient and mosaic. Colors of polygons on a color gradient cartogram smoothly changes from one up to other color depending on value of the analyzed characteristic. For construction of a gradient solid you can use up to 7 primary colors. In case the gradient is formed by one color, polygons will be painted in shades of one color (from white up to black with transition through the specified color). On a mosaic cartogram polygons are painted into at random chosen colors. Construction of color cartograms can be made and on linear objects. It is possible to paint, for example, into different colors the electrified and not electrified railways. Linear color cartograms also can be used, for example, for a fast visual estimation of coincidence of semantic characteristics of adjacent objects on border of the joined neighbour sheets. If to paint contours into different colors according to the characteristic «absolute height» at visual viewing it is possible to define presence of a mistake quickly. On a hatched cartogram the image of polygons differs due to selection of various type of shadings, distance between lines and thickness of lines of shading. On a point cartogram the image of polygons differs due to selection of the size of filling points and distance between points. The type of a created cartogram (color (fill), strobe, point) is chosen by pressing the corresponding button. To processing in the given procedure the objects are exposed which were preliminary selected on an initial electronic map (for example, by means of search and mark). The information according to which the selected objects of a map will be painted, can be contained in semantics of objects, in the table of the user database of type .dbf or in text files .txt. For creation of thematic maps both tables preliminary connected to a map and tables not having links with a map can be applied. Linked tables are characterized by presence in their structure of fields LINKSHEET and LINKOBJECT, containing references to concrete objects of a concrete map. In LINKSHHET field the sheet nomenclature (the conditional name) is stored on which the object corresponding to the given record is located, and in LINKOBJECT field - its unique number. However, if you use the table in which direct links with objects of a map are not established, it is necessary to provide an opportunity of an establishment of such link. It means, that in semantics of the selected objects there should be values (binding semantics), which unambiguously can be compared with values of a corresponding field of concrete record of the processed table (a binding field). For example, you have map of administrative division of Russian Federation where regions are submitted as the polygons, having in semantics a code (number) of corresponding region, and the summary table of the information on regions, one of which fields - a code of region. Link can be established both by numerical, and by character values (for example, the Name of region), unique restriction is that the binding semantics and the binding field should have identical type (both numerical or both character). The window of procedure dialog contains 3 bookmarks (Data, View and Legend). The sequence of bookmarks corresponds to sequence of actions at creation of a thematic cartogram, i.e. for successful execution of procedure it is necessary consistently to enter all bookmarks, since Data and finishing Legend and to make corresponding settings.
|
